Poker: Texas Hold'em (No Limit) Your game will start after this ad. You must sign in to play this game. Log in to play with your friends! Play as a guest Sign in.
Full ring poker tables, or those with a 9 or 10-player max, are a good place to learn no-limit Texas holdem. The reason why is because you don’t see the blinds as often, meaning full ring tables are a cheaper way to practice.
But most players don’t remain exclusive to these games. They often branch out to shorthanded tables, either for a different cash game experience or because they’re forced to in tournaments.
Shorthanded poker requires a different approach than full ring, because you’re dealing with fewer players. But the upside is that you can also make more money due to a greater volume of hands.
If you’re new to shorthanded poker, keep reading as I cover everything a beginner should know. Specifically, I’ll discuss more about this game, why you should play smaller tables, and what shorthanded Texas holdem strategy is.
What is Shorthanded Texas Holdem?
A shorthanded poker table features 6 or fewer players. You’ll also see these tables referred to as 6-max games.
6-max cash games never allow more than six players to enter the game. You’ll see a good number of these in online poker lobbies.
Poker tournaments begin with full ring tables, but they see shorthanded tables develop as more players are eliminated.
One of the tournament director’s jobs is to spot these shorthanded tables and consolidate them with larger tables.
6-max games play faster than full ring tables in both live and online play. Here are some common averages for different types of poker tables.
- 6-max online table = 80 hands per hour
- Full ring online table= 60 hands
- 6-max live table = 30 hands
- Full ring live table = 20 hands
Why Should You Play Shorthanded Texas Holdem?
Here are the three best reasons to play shorthanded Texas holdem.
- More action.
- Less folding.
- More hands per hour for profitable players.
Many recreational poker players become bored with folding hand after hand. But this is the dynamic in full ring games, because more players mean the potential for a stronger winning hand.
Tables with six or fewer players don’t see as strong of winning hands. This means that you can play a wider range of cards and still have a chance of taking the pot down.
Shorthanded holdem players will appreciate the fact that they won’t be folding as many hands on average.
If you’re a successful holdem player, then you’ll also like how shorthanded games can increase your profits. The fact that you see more hands also means that you have additional chances to win money.
How Does Shorthanded Texas Holdem Differ from Full Ring Holdem?
Starting Hands In Texas Holdem
I’ve already covered the basics of how shorthanded Texas holdem differs from full ring games. But how does the overall strategy and gameplay change?
The biggest strategy change comes with what kind of starting hands you should be willing to play.
A tight-aggressive (TAG) approach works best in full ring games, where you can sit back and play premium hands. But the blinds will really eat your chip stack in shorthanded cash games and tournaments.
For example, you might not normally raise with AJ in middle position on a 9-player table. But this can be a good hand to raise within a shorthanded game.
It’s good to be aggressive on the button in unraised pots. But this is especially important on smaller tables, where raising with any decent hand can take the pot down.
Overall, 6-max games play faster and more aggressively than what you’ll see at full ring tables. Furthermore, many of these shorthanded pots are won before the flop.
Strategy for Short Handed Texas Holdem
The general strategy between full ring and shorthanded holdem is that the latter requires more aggressive play.
Of course, this doesn’t tell you anything specific. This is why I’m going to cover 7 tips that all shorthanded Texas holdem beginners should know.
1 – Play Tight in the Beginning
This tip contradicts what I’ve discussed so far. Nevertheless, you should play almost as tight as you do in full ring games when starting out in shorthanded holdem.
Playing aggressively leads to more losses for players that don’t have a good feel for smaller tables. And inexperienced 6-max players sometimes get carried away by playing too many hands.
Note:A good full ring player only plays around 15-20% of their hands on average. A good shorthanded player will play 25-35% of their hands.
The number of hands you play shouldn’t increase by a tremendous amount, such as 45-55%. Instead, you want to gradually increase your playable hand range.
A beginner should focus on playing premium hands, along with a few hands outside the lines of big pocket pairs, mid pocket pairs, and high suited connectors.
The goal is to increase your playable hand range as you become more confident in your skills and in analyzing opponents. I’ll discuss more on what hands you should play in Tip #3.
2 – Raise into Hands – Don’t Limp
One of the keys to becoming a successful poker player is realizing that your strategy should vary based on opponents and the table dynamic. But a good general poker strategy rule is that you want to make preflop raises into unopened pots, or those that haven’t seen a raise yet.
Here are three goals that you accomplish by raising preflop in unopened pots:
Opening Hands Holdem
- You show hand strength.
- You force players to pay to see the flop.
- You build fold equity for post-flop play.
Beginning with the first point, raising shows players that you likely have a strong hand. Therefore, they’re less likely to try and bluff you out of the pot.
Regarding the second goal, you want to limit the number of players who see the flop when you have a strong hand.
Your goal should be to isolate a single player so that you have a better chance of winning the hand if it goes to the showdown. Contrast this to multiple players seeing the flop, which decreases the chances that your strong cards will eventually win the hand.
The best way to thin the field out is with a raise worth 3x the big blind (bb). This is just enough to where few players won’t call with speculative hands, but also low enough to where you can get out of the hand cheaply when re-raised.
Of course, I’m not saying that you should fold to every re-raise. But if you’re holding pocket jacks or AK and worried that somebody has a better hand, you won’t feel as bad about sacrificing 3xbb.
As for the third goal, building fold equity increases the chances that you can take down the pot before the showdown.
This goes back to the first point of showing hand strength. When players believe that you have a good preflop hand, they’re more likely to think that you’ll flop a strong hand.
This sets you up for good continuation betting (c-betting) scenarios in case you miss the flop. A c-bet combined with fold equity is more likely to convince your opponent to fold and help you take the pot.
Limping is a passive move that doesn’t show hand strength or build fold equity. Furthermore, it’s likely that you’ll be re-raised by somebody who thinks they can steal the pot.
It makes sense to limp into pots in specific situations, like when your table is full of calling stations whom you can out-play post-flop. But most of the time, you should either fold, raise, re-raise, or call a raise/re-raise.
3 – Play in Position
The most desirable position to be in on any poker table is the dealer’s seat (a.k.a. the button) because you act last after other players. This means you have more info on opponents and can use their betting actions to judge their hand strength.
In contrast, the worst spots to be in are the seats closest to the dealer’s left (a.k.a. early position). Anybody raising from the spots should have good hand strength because they must make their bets before anybody else.
Here are the different table positions in a 6-max game:
- Early position = Small blind, big blind, seat to big blind’s left (under the gun or “UTG” ).
- Middle position = Seat to UTG’s left.
- Late position = Seat to the button’s right (a.k.a. the cut-off or “CO”) and the button.
The great thing about playing from the CO and late position is that you act after other players. If an early position TAG player makes a 3x-4xbb raise, you can fold something like KQs that you might otherwise play.
Early position is at a huge disadvantage because they could easily be re-raised by a later player. This is why you should narrow your hand range from this spot and avoid playing speculative hands.
The blinds act last before the flop. But they’re still considered early position because they act before everybody post-flop.
Middle position is aptly named because they’re sitting in an in-between spot. You can raise with a wider range here in unopened pots, but you still need to worry about the button and CO.
You’ll see table position play a heavy factor in the starting hand advice listed below.
4 – Follow a Starting Poker Hand Chart
I can’t stress enough how important is to base your strategy on the situation. This means that you shouldn’t always have a strict strategy for starting hands.
But a starting hand chart helps immensely in the beginning as you learn shorthanded Texas holdem.
If you’re coming from full ring holdem, or you’re new to poker overall, then you won’t have a good idea on what starting hands to play. But by following a chart, you can quickly master what hands play well on a shorthanded table.
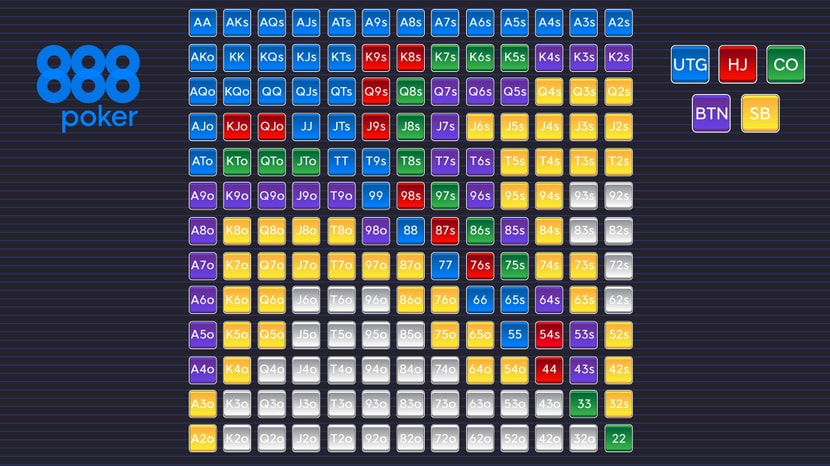
Here’s a starting hand chart that shows when to raise, call, and 3-bet from each 6-max position. (Note that “s” means suited.)
Small Blind
- Raise = AA, KK, QQ, JJ, TT, 99, AKs, AK, AQs, AQ, AJs, AJ, KQs
- Limp = 88, 77, 66
- 3-bet (third bet on a street) = AA, KK, QQ
Big Blind
- Raise = AA, KK, QQ, JJ, TT, 99, AKs, AK, AQs, AQ, AJs, AJ, KQs
- Limp = N/A
- 3-bet = AA, KK, QQ
Under the Gun
- Raise = Most pocket pairs (AA to 44), AKs, AK, AQs, AQ, AJs, AJ, KQs
- Limp = No hands
- 3-bet = AA, KK, QQ
Middle Position
- Raise = Any pocket pair (22+); suited ace hands from AKs to A9s; offsuit ace hands from AK to AJ; and KQs, KQ, QJs
- Limp = Low pocket pairs (a.k.a. “set mining”); AKs, AK, AQs, AQ, KQs
- 3-bet = AA, KK, QQ
Cut-off
- Raise = Any pocket pair (22+); suited ace hands from AKs to A6s; offsuit ace hands from AK to AT; other suited hands from KQs to T8s; and other offsuit hands from KQ to JT
- Limp = Middle and lower pocket pairs
- 3-bet = AA, KK, QQ, JJ
Button
- Raise = Any pocket pair (22+); any suited Ax combo; offsuit ace hands from AK to A9; other suited hands from KQs to 86s; other offsuit hands from KQ to T9
- Limp = Middle and lower pocket pairs
- 3-bet = AA, KK, QQ, JJ
You can see that there’s an overlap in hands you should raise and limp with regarding certain suited connectors and pocket pairs. I suggest either raising or folding these overlapping cards (no limping) until you have a better understanding of your opponents and the table dynamic.
Also note that these starting hands are for a shorthanded table with six players. You should loosen up your starting hand requirements even more when there are 5 or fewer players.
5 – Gradually Become More Aggressive
A starting hand chart should only serve as a base when learning shorthanded Texas holdem. The ultimate goal is to open up your play and take advantage of more opportunities.
This allows you to steal more pots and blinds, which is crucial with blind orbits coming around more often.
But the key is to gradually become more aggressive, rather than forcing raises and re-raises just to create a looser table image. Too many beginners read about becoming more aggressive, then force the action.
New shorthanded players should instead let their aggression come naturally as they gain experience. You’ll eventually recognize certain situations that allow you to open up your hand range and take advantage of the situation.
One great thing about playing aggressively is that it allows you to win pots through two ways.
- Forcing opponents to fold.
- Having the best hand at the showdown.
If you’re only limping into pots and calling raises, then you can’t win uncontested pots. Instead, you need to rely on having the best cards in these situations.
Once again, the key is to gain experience at shorthanded tables before opening up your hand range.
Start out by playing tight on shorthanded tables (Tip #1), then continue observing situations where it’s profitable to play aggressively with a wider range of hands.
6 – Changing Gears when Tournament Play Becomes Short Handed
You’ll run into shorthanded situations as poker tournaments move along. This is especially the case if you play online sit and go’s (SNGs), which consist of a single table.
You’ll also experience situations where play goes from shorthanded to full ring when multi-table tournaments consolidate tables.
In either case, you need the ability to change gears once play becomes full ring or shorthanded.
Full ring play requires a tighter style and starting hand requirements. The reason why is because you need a better overall hand to win in these situations.
But you should open up your play as soon as you see the table reduced to six or fewer players. This isn’t overly difficult as long as you’re paying attention and remember that you need to switch up your play on shorthanded tables.
It pays to be experienced with both full and 6-max up tables when making this happen. This is why I suggest that tournament players spend time in all different types of tourneys, so they can develop these skills.
MTTs start with full ring tables and see shorthanded tables develop along the way. But you can also find online 6-max tournaments that allow you to practice shorthand play.
As mentioned before, SNGs are great for practicing the transition from full ring to shorthanded play. You don’t have to play deep into SNGs to experience 6-max play, because they end relatively quickly.
Cash games make for good practice too, whether you need to work on 6-max or full ring play. But these aren’t perfect when practicing for tournaments, because you’re not dealing with short-stacked situations.
Cash players can reload their chip stacks at any time. Tournament players, on the other hand, are dealing with finite stacks.
This is why it’s nice to get specific experience in shorthanded tourney play. Doing so combines different stack sizes with the aggressive play that happens on 6-max tables.
7 – Always Consider that Your Opponent may Have Something
One more tip for shorthanded Texas holdem is to always consider that opponents can have a hand.
Shorthanded tables feature more semi-bluffing and pot stealing on a per-hand basis. But this doesn’t mean that players are bluffing every other hand.
You should assume that a player has good cards until you have more information on them. Don’t fall into the trap of worrying about bluffs just because 6-max players are more aggressive.
Keep an eye on your opponents and study their tendencies. If a TAG player is betting aggressively from early position, then it’s a sign that they probably have a great starting hand.
You’re better off folding and assuming they have something, rather than losing a much-bigger pot later on.
But if a loose-aggressive player is constantly trying to steal the blinds from late position, there’s a chance that they’re semi-bluffing.
The key is to build profiles on your opponents, then use this info to catch the small percentage of the time when you‘re being bluffed.
Conclusion
Poker fundamentals transition well across tables of any size. But you should still note the key differences when moving from a full ring to a shorthanded table.
The main thing that you should do is play more hands on 6-max tables. This helps you counteract the greater frequency of blinds and win more uncontested pots.
Beginners should slowly transition into being more aggressive. Use the starting hand chart that I covered before until you develop a good feel for 6-max play.
Of course, individual tables will call on you to vary your strategy based on the situation. And this is where experience helps you adapt to different situations.
In summary, shorthanded Texas holdem is a faster-paced game that’s really fun once you get the hang of the strategy. And if you become really good at these tables, you’re going to make even more money due to playing more hands per hour.
One of hold’em’s most crucial decisions is, do I see the flop or don’t I see the flop? In this lesson we’ll examine the importance starting hand selection and what factors you need to consider before deciding whether to hold’em or fold’em.
There are 169 different two card starting hand combinations in hold’em poker. This number assumes, for the sake of argument, that is the same as , or any other suited combination. If you are not dealt a pair, then your starting hand will either be suited or unsuited, and either connected or unconnected (gapped). This means your starting hand will fall into one of the following five categories:
- Pairs – e.g. , ,
- Suited connectors – e.g. , ,
- Connecting cards – e.g. , ,
- Suited unconnected cards – e.g. , ,
- Unconnected cards – e.g. , ,
Unconnected cards might be one, two, three-gapped, or more. The bigger the gap, the less chance you have of hitting a straight. For example, if you hold 73, then you’d need a flop of 456 for the straight. But holding T8, you could flop a straight with 9JQ or 679.
The Best Starting Hands in Hold’em
Let’s start by talking about the best starting hands, which are often referred to as ‘premium hands’. There is some disagreement amongst poker players as to which starting hands are the best, but few would dispute the value of the first of our three main groups, Aces and Kings.
Group 1: AA, KK
These two starting hands are the major players in hold’em. It’s not often you’ll get dealt Aces or Kings. In fact you get either Aces or Kings once in every 110 hands, so it’s not nearly as often as we’d like. Aces are by far the best possible starting hand in hold’em, closely followed by Kings. However, you should be aware that even Aces or Kings can get cracked, and they don’t play too well against multiple opponents. This means you should definitely be raising pre-flop to narrow the field. Extra caution is necessary when playing Kings, because if an Ace falls on the flop then you’re losing to anyone who has a single Ace in their starting hand. While they are very strong hands which most players love to get, they are certainly not unbeatable.
Group 2: QQ, JJ, AKs
Queens and Jacks are great starting hands, and with either of these, you can usually be confident you have the best starting hand. Of course they are dominated by Aces and Kings, but they’re a favourite against all other starting hands. While Queens and Jacks will occasionally run into a player holding either Aces or Kings, it doesn’t happen too often. Play these cards strongly, and always look to raise with them.
Ace-King is known throughout the poker world as Big Slick, and when suited it’s often called Super Slick. While it isn’t a ‘made hand’, unlike a pair, it offers great potential. It’s only a big underdog to Aces and Kings, and even pairs like Queens and Jacks are only slight favourites. The beauty of AK (suited or unsuited), is that it dominates so many other hands like AQ, AJ, AT, and so on. These types of hands are the ones that players usually end up pushing all-in with late in a tournament.
Group 3: TT, AK, AQs, AJs, KQs
This next group of starting hands is also a strong bunch. You should definitely be looking to raise pre-flop with any of these hands too. We’ve already talked about the power of AK, but starting hands like AQs, and AJs, are also very strong and often run into weaker Ace-X combinations. Even though these are all strong starting hands, and most of the time you’ll be winning pre-flop, you have to be careful – particularly a hand like KQs, which you can easily fold to a re-raise.
Suited Cards
You’ll often hear novice players responding to questioning of why they played a particular starting hand with the line “well, because they were suited”. Some suited cards are worth playing and it’s certainly better to start with suited cards than unsuited cards. However, the odds of flopping a flush is 1 out of 118 hands (0.8%) with two suited cards, and you’ll only make a flush after the river around 6.5% of the time. Don’t fall into the trap of playing any two cards just because they happen to be suited – it doesn’t make a big enough difference to make junk hands valuable.
Kicker Issues
The word ‘kicker’ means the smaller of your two cards. Some players play a hand if it contains an Ace with any other card (such as an Ace with a 3 kicker), and this type of play ultimately cost players money and tournaments. For example, let’s suppose a player calls with A6 and the flop comes A83. What does the player do? bet? call? raise? call a big raise? go all-in? What if the flop comes Q63? The player has middle pair – which is very hard to play. Hey, the flop could come A6X – the player has two pair, Aces and sixes but this happens only 1 out of 49 hands (2%). Until you learn when and how to play Ace junk (AX) go slow with it. One good thing about A junk and K junk, is that you do not need to play these hands to learn when they may be profitable. Let experience from other hands and study be your teacher.
Table Conditions
Hold’em starting hands can be a complex subject because every situation is different. If you were to ask a professional poker player, “should I call, raise, or fold this hand pre-flop?” his response would almost certainly be “it depends!” Here are some of the main reasons why it depends:
The Number of Players
The value of certain starting hands is very dependent upon the number of players at the table. Certain starting hands are always going to be under threat against a table of nine or ten players, but the value of these same hands increases when there are fewer players. A starting hand like KJ might be vulnerable against a full table of players, but is considered a strong hand if there are just a few other players.
Position
Your position on the poker table will be a major factor in deciding which starting hands you should play. The later your position in the betting order, the better – because you get to decide what to do after most of your opponents have acted. We’ll talk much more about the importance of position throughout our lessons on Pokerology, but as a first step please see our lesson on the value of position. Playing position can elude us at first because it is a part of poker that lends itself to be exploited through experience. However, you must quickly realize that your position at the table should heavily influence the choice of starting hands that you play. Until a player has a feel or grasp for positional play, just believe and follow some of the suggestions on the subject.

A Raised Pot
Whether or not a pot has been raised should be a very important factor in your decision to play a particular starting hand. Your selection of starting hands should change when the pot has been raised by a reasonable player. If there has been a raise and a re-raise before you’re due to act, then you should only consider playing with a very strong hand. Of course this will also depend on the personality types of the other players and whether the game is very loose or passive.
Starting Hand Charts
When you first start playing poker it can be helpful to use a starting hand chart as a point of reference. We’ve created a couple of starting hand charts that can be used by beginners. Please click on the following links to view these charts (they will open in a new window):
Each of these charts loads as a PDF, meaning they be viewed on screen, bookmarked or better still, can be printed and studied offline.
Beginners can treat starting hand charts as the gospel, but once you know enough about the game to recognize appropriate opportunities, you can deviate because your adjustment may represent a more profitable play. Our starting hand charts are a guide, not a set of intractable rules. There is no such thing as a perfect starting hand chart, because every game is different and there are many variables at work. Game texture and table conditions can’t be measured and included into a neat formula.
There are many factors that may encourage you to tighten or loosen your play from our guidelines. If you have a starting hand that’s not listed on the chart, then there’s a good reason – it should almost always be mucked. But as in all poker decisions the phrase, “It depends” comes to mind. However, before you decide to deviate from our guidelines, have a reason for taking such an action.
Conclusion
Don’t fall into the trap of playing any two cards. Most poker players want to play hands and as a beginner it’s very easy to be seduced by suited cards or picture cards, or any two-card holding that contains an Ace of a King – but if you play hold’em correctly, you’re going to be selective and toss away the vast majority of hands you’re dealt.
When you gain more poker playing experience you can begin to open up your range of starting hands – but until then, proceed with caution and only play the best hands. Loose, promiscuous play will get you into trouble and is the downfall of many players.
In future lessons we’ll expand much more on the topics discussed in this poker lesson and get you to think beyond the actual cards you’re dealt. We also have hours of video footage covering starting hand selection for both no-limit and fixed-limit hold’em – so depending upon your preference, be sure to check them out!
Related Lessons
By David Sasseman
David lives in Atlanta, Georgia, and has played over a million hands online and many thousands of hands in Mississippi, Louisiana, Florida, Illinois, Indiana, and Las Vegas casinos.